
Introduction
Sleep plays a vital role in our overall health and well-being. It is a natural process that allows our body and mind to rest and rejuvenate. However, in today's modern world, our sleep patterns are often disrupted due to various factors, one of which is light.
Light has a significant impact on our sleep quality and our body's natural sleep-wake cycle, also known as the circadian rhythm. Exposure to light at the wrong times, such as during the night or early morning, can disrupt our sleep and leave us feeling tired and groggy.
Research suggests that exposure to light at night can have several negative effects on our health. It can increase the risk of obesity, disrupt our circadian rhythm, and even damage our vision. Understanding how light affects our sleep is essential for ensuring we get the quality rest we need.
This article will explore the impact of light on sleep and provide practical tips on how to sleep better in the dark. We will discuss the role of melatonin in sleep regulation, the types of light that affect sleep, and the importance of darkness for quality sleep. We will also provide methods and techniques to create a dark sleep environment, including using curtains or blinds effectively, wearing an eye mask, and avoiding electronic devices before bed.

Disruption of Sleep Quality
Disruption of sleep quality can have a significant impact on overall health and well-being. When our sleep is disrupted, we may experience difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or waking up feeling refreshed. This can lead to daytime drowsiness, lack of focus, and decreased productivity.
There are several factors that can contribute to the disruption of sleep quality, including exposure to light at night. Light exposure, especially blue light emitted by electronic devices and LED lights, can interfere with the body's natural sleep-wake cycle.
Studies have shown that exposure to light before bedtime can suppress the production of melatonin, a hormone that regulates sleep. When melatonin levels are disrupted, it can make it harder for us to fall asleep and stay asleep throughout the night.
Additionally, light exposure during the night can also disrupt the circadian rhythm, our internal body clock that regulates sleep and wakefulness. The circadian rhythm relies on darkness to signal the body to release melatonin and prepare for sleep. When we are exposed to light at night, it can confuse our body's natural sleep signals and make it more difficult to achieve deep, restorative sleep.
Poor sleep quality has been linked to a variety of health issues, including an increased risk of obesity. Lack of sleep can affect hormones that control hunger and appetite, leading to an increased desire for high-calorie foods. It can also disrupt the metabolism, making it harder for the body to process and burn calories.
In addition to its impact on sleep and weight, excessive light exposure at night may also have potential damage to vision. Studies have suggested that long-term exposure to blue light can contribute to the development of age-related macular degeneration, a leading cause of vision loss.
Ensuring a dark sleep environment is crucial for maintaining healthy sleep patterns and promoting quality rest. Creating a dark sleep environment can involve using curtains or blinds to block out external light sources, wearing an eye mask to shield the eyes from light, and avoiding electronic devices before bed.
By understanding the impact of light on sleep and implementing strategies to sleep better in the dark, individuals can improve their sleep quality and overall well-being.

Disruption of Circadian Rhythm
Disruption of circadian rhythm is a common issue that can significantly affect sleep quality. The circadian rhythm is the 24-hour internal clock that regulates various physiological and behavioral processes in our bodies, including sleep-wake cycles.
Exposure to light, especially blue light emitted by electronic devices and energy-efficient LEDs, can disrupt the circadian rhythm. This is because our brains interpret blue light as daylight, signaling the body to stay awake and alert.
When we are exposed to light at night, it suppresses the production of melatonin, a hormone that helps regulate sleep. This suppression can confuse the circadian rhythm, making it difficult to fall asleep and stay asleep throughout the night.
Disrupted circadian rhythm can lead to various consequences. It can cause difficulties falling asleep, resulting in insomnia or poor sleep quality. It can also impact the timing of sleep, making it difficult to maintain a consistent sleep schedule. This can lead to fatigue and daytime sleepiness.
Furthermore, disruption of the circadian rhythm can affect other aspects of our health. It has been linked to an increased risk of developing chronic conditions such as obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and mood disorders.
It is important to be mindful of the impact of light on our circadian rhythm and take steps to minimize exposure to artificial light, especially during the evening and nighttime hours. Creating a dark sleep environment, using curtains or blinds effectively, wearing an eye mask, and avoiding electronic devices before bed are some effective methods to promote a healthy circadian rhythm and improve sleep quality.
Increased Risk of Obesity
Disruption of sleep quality can lead to an increased risk of obesity. Research has shown that inadequate or poor sleep can contribute to weight gain and difficulty in losing weight. There are several factors that link poor sleep with obesity.
One factor is the disruption of hormonal regulation that occurs when sleep is disturbed. Sleep deprivation can alter the production and regulation of hormones such as leptin and ghrelin, which are responsible for appetite control. Lack of sleep can cause an increase in ghrelin, a hormone that stimulates hunger, while decreasing levels of leptin, a hormone that signals fullness. This hormonal imbalance can lead to increased food cravings, especially for high-calorie and carbohydrate-rich foods, which can contribute to weight gain.
Additionally, inadequate sleep can affect the body's metabolism. Sleep deprivation can lower metabolic rate and reduce energy expenditure. This means that the body burns fewer calories at rest, making it easier to gain weight. It also impairs the body's ability to process glucose efficiently, which can increase the risk of insulin resistance and diabetes.
Furthermore, poor sleep can lead to increased stress levels. When individuals are sleep deprived, their bodies produce higher levels of the stress hormone cortisol. Elevated cortisol levels can lead to increased appetite, especially for unhealthy, high-fat foods. This can further contribute to weight gain and obesity.
In conclusion, disrupted sleep quality can have significant implications for weight management and obesity. It is important to prioritize sleep and establish healthy sleep habits to minimize the risk of weight gain and promote overall well-being.

Potential Damage to Vision
Exposure to excessive light can potentially damage vision and have long-term effects on eye health. The eyes are sensitive organs that rely on a delicate balance of light and darkness to function optimally. When exposed to bright light for extended periods, such as artificial light from electronic devices or excessive ambient light in the environment, the eyes can experience various negative effects.
One of the primary concerns regarding potential damage to vision is the increased risk of developing age-related macular degeneration (AMD). AMD is a progressive eye disease that affects the central vision, making it difficult to see fine details and perform tasks like reading or driving. Studies have shown a strong link between excessive light exposure, particularly blue light emitted by electronic devices, and the development of AMD.
Another issue related to prolonged light exposure is the potential for retinal damage. The retina is the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye that plays a crucial role in transmitting visual information to the brain. Overexposure to bright light can lead to oxidative stress and the production of free radicals, which may damage the retinal cells and contribute to vision problems.
In addition to these long-term effects, excessive light exposure can also cause immediate discomfort and temporary vision disturbances. For example, staring at a bright screen or being in a well-lit environment for too long can lead to eye strain, dryness, and irritation. These symptoms, commonly known as digital eye strain or computer vision syndrome, can affect both children and adults who spend extended periods in front of screens.
To protect vision and reduce the potential damage caused by excessive light exposure, it is essential to prioritize proper light management techniques. This includes minimizing exposure to bright lights, especially before bedtime, and creating a dark sleep environment to ensure adequate rest for the eyes and the body.
By implementing strategies such as using curtains or blinds effectively, wearing an eye mask, and avoiding electronic devices before bed, individuals can promote better sleep and protect their vision. Developing healthy habits surrounding light exposure can have significant benefits for overall eye health and quality of life.
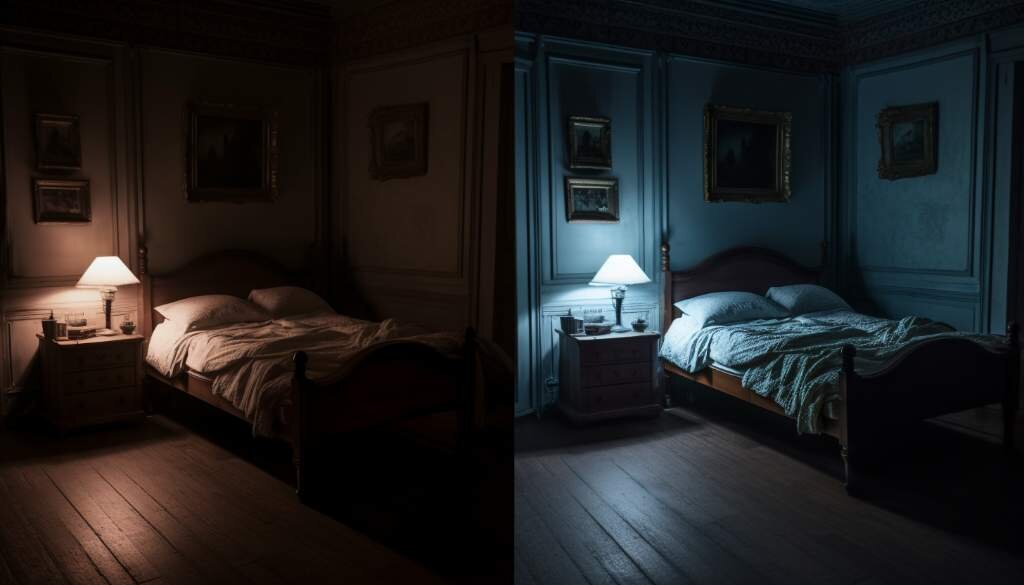

How Light Affects Sleep
Light plays a significant role in our sleep patterns and overall sleep quality. How light affects sleep is a topic that has gained a lot of attention in recent years. In this section, we will explore the various ways in which light can impact our sleep.
We will begin by discussing the role of melatonin, a hormone that helps regulate our sleep-wake cycle, and how light can interfere with its production. Next, we will delve into the types of light that have the most significant impact on our sleep, including natural and artificial sources.
Additionally, we will highlight the importance of darkness for quality sleep and how exposure to light, especially before bedtime, can disrupt our sleep patterns. We will explore the negative effects of light exposure on the duration and quality of our sleep. Lastly, we will provide practical tips and methods to sleep better in the dark, such as creating a dark sleep environment, using curtains or blinds effectively, wearing an eye mask, and avoiding electronic devices before bed.
Role of Melatonin in Sleep Regulation
Melatonin is a hormone that plays a crucial role in regulating sleep. It is produced by the pineal gland in the brain, mainly in response to darkness. This sub-section explores how melatonin influences sleep and the importance of its regulation.
When it starts getting dark in the evening, the pineal gland begins to release melatonin into the bloodstream. This increase in melatonin levels signals to the body that it is time to sleep and helps to regulate the sleep-wake cycle, also known as the circadian rhythm.
One of the key functions of melatonin is to help regulate the timing and duration of sleep. It promotes feelings of sleepiness, helping individuals fall asleep faster and maintain a more restful sleep throughout the night. Melatonin levels typically rise in the evening and remain elevated during the night, before gradually decreasing towards the morning.
Exposure to light, especially blue light from electronic devices or bright artificial lighting, can suppress the production of melatonin. This can disrupt the natural sleep-wake cycle and make it more difficult to fall asleep or stay asleep. It is important to limit exposure to artificial light in the evening, especially before bedtime, to allow melatonin levels to rise and promote quality sleep.
Disruptions in the production of melatonin can have a significant impact on sleep quality and overall well-being. Shift workers or individuals who frequently travel across time zones often experience disturbances in melatonin production due to irregular sleep schedules and exposure to light at inappropriate times. These disruptions can lead to sleep difficulties, daytime fatigue, and even mood imbalances.
To help regulate melatonin production and promote quality sleep, it is important to establish a bedtime routine that includes creating a dark sleep environment. This can be achieved by using blackout curtains or blinds to block out external light sources, wearing an eye mask to further enhance darkness, and avoiding the use of electronic devices that emit blue light before bed.
In conclusion, melatonin plays a vital role in sleep regulation by signaling the body when it's time to sleep. Maintaining healthy levels of melatonin through proper light management is essential for a good night's sleep and overall well-being.
Types of Light that Affect Sleep
Light plays a significant role in regulating our sleep patterns. Different types of light can affect our sleep quality and disrupt our circadian rhythm. Understanding the types of light that impact sleep can help us make informed decisions about our sleep environment. Here are some of the main types of light that can affect sleep:
- Blue Light: Blue light is emitted from electronic devices such as smartphones, tablets, and computers, as well as energy-efficient light bulbs. It suppresses the production of melatonin, a hormone that regulates sleep, making it harder to fall asleep and maintain a deep sleep. Exposure to blue light before bed can lead to sleep disturbances and insomnia.
- White and Bright Light: Exposure to bright or white light during the evening or nighttime can interfere with the body's natural circadian rhythm. It tricks the brain into thinking it's still daytime, suppressing melatonin production and delaying sleep onset. This type of light is commonly found in outdoor streetlights and indoor lighting.
- LED Lights: LED lights are commonly used for energy-efficient lighting in homes and workplaces. While they offer many benefits, certain LED lights emit high levels of blue light, similar to electronic devices. It's important to choose LED lights with warm or cool color temperatures to minimize the impact on sleep.
- Red Light: Unlike blue light, red light has a minimal impact on melatonin suppression. It is commonly used in night lights and sleep-friendly lamps. Red light helps maintain the body's natural sleep-wake cycle and is ideal for creating a sleep-friendly environment.
By understanding the different types of light that can affect sleep, we can make adjustments to our sleep environment to promote better sleep. Minimizing exposure to blue light, particularly from electronic devices, in the evening, and opting for warm or cool LED lights or red light can help regulate our sleep-wake cycle.
Importance of Darkness for Quality Sleep
The importance of darkness for quality sleep cannot be overstated. Our bodies are biologically programmed to sleep when it is dark and be awake when it is light. Darkness signals the brain to release melatonin, a hormone that regulates our sleep-wake cycle. Here are a few reasons why darkness is crucial for quality sleep:
- Promotes Melatonin Release: Melatonin is a hormone produced by the pineal gland in the brain. Its production is triggered by darkness and inhibited by light. When it gets dark, the brain releases melatonin, which helps to regulate our sleep-wake cycle and promote deep, restorative sleep.
- Enhances Sleep Quality: Exposure to light, particularly blue light emitted by electronic devices, before bed can suppress melatonin production and disrupt our circadian rhythm. This can lead to difficulty falling asleep and poor sleep quality. Creating a dark sleep environment ensures that our bodies can naturally produce melatonin and improve the quality of our sleep.
- Reduces Sleep Disturbances: Bright lights, even from street lamps or electronic devices, can interfere with our sleep. Light exposure during the night can cause awakenings and disturbances in our sleep cycles. Sleeping in a dark environment minimizes these disruptions, allowing for uninterrupted sleep.
- Regulates Biological Clock: Darkness plays a crucial role in syncing our internal biological clock with the external environment. This synchronization is essential for maintaining a healthy sleep-wake cycle. Exposure to artificial light during the night can confuse the body's internal clock and disrupt its natural rhythm.
- Improves Overall Sleep Duration: Studies have shown that exposure to light, even low levels, during the night can decrease total sleep duration. Creating a dark sleep environment helps to ensure a longer and more restful sleep.
To promote quality sleep, it is important to create a dark sleep environment. This can be achieved by:
- Eliminating External Light: Use blackout curtains or blinds to block out any external light sources from streetlights or cars. Ensure that your curtains are thick enough to prevent any light from seeping in.
- Minimizing Electronic Devices: Avoid using electronic devices that emit blue light, such as smartphones and tablets, before bed. If you need to use them, enable night mode or use blue light-blocking apps to reduce the impact on melatonin production.
- Using an Eye Mask: For those who cannot control external light sources, using an eye mask can help create complete darkness and promote better sleep.
- Maintaining a Consistent Sleep Schedule: Going to bed and waking up at the same time every day helps regulate the body's internal clock and promotes better sleep. This consistency helps the body anticipate sleep and naturally prepare for it.
- Using Dim Lights: Before transitioning to sleep, use dim lighting in your bedroom to signal to your body that it is time to wind down. This can be achieved through the use of low-wattage bulbs or dimmer switches.
By prioritizing darkness in our sleep environments, we can significantly improve the quality and duration of our sleep, leading to better overall health and well-being.

Methods to Sleep Better in the Dark
Methods to Sleep Better in the Dark are strategies and techniques that can help improve the quality of sleep by creating a dark sleep environment. Darkness plays a crucial role in regulating our sleep-wake cycle and ensuring a restful night's sleep. In this section, we will explore various methods that can promote better sleep in the dark.
We will start by discussing the importance of darkness for quality sleep and how light affects our sleep patterns. Then, we will delve into the role of melatonin, a hormone that regulates sleep, and the types of light that can disrupt its production. Next, we will explore different ways to create a dark sleep environment, including using curtains or blinds effectively, wearing an eye mask, and avoiding electronic devices before bed.
Creating a Dark Sleep Environment
To create a dark sleep environment, there are several steps you can take to minimize light exposure and optimize your sleep environment:
- 1. Cover windows: Use blackout curtains or blinds to block out external light sources. These types of window coverings are designed to prevent light from seeping through and can significantly darken your bedroom.
- 2. Seal off light sources: Make sure there are no electronic devices, such as TVs, computers, or digital alarm clocks, emitting light in your bedroom. Use tape or covers to block any small LED lights that may be present on these devices.
- 3. Use dim lighting: Before bed, switch to dim, warm lighting in your bedroom. Avoid bright overhead lights and instead opt for bedside lamps or dimmable lighting options.
- 4. Remove or cover electronic devices: If you have electronic devices in your bedroom that cannot be turned off or covered, consider using a sleep mask to block any light they emit.
- 5. Use heavy curtains or blinds: In addition to blackout curtains, consider using heavy curtains or blinds to further block out light. This can be especially helpful if your bedroom is exposed to streetlights or other sources of outdoor light.
Using Curtains or Blinds Effectively
Using curtains or blinds effectively is an important aspect of creating a dark sleep environment. Properly utilizing these window coverings can help block out unwanted light and improve the quality of your sleep.
When it comes to curtains, opt for ones that are made of thick, opaque fabric. This will help prevent any light from seeping through. Additionally, choose curtains that are long enough to reach the floor and wider than your window frame. This ensures that there are no gaps for light to enter.
If you prefer using blinds, consider blackout blinds. These blinds are specifically designed to block out light and are highly effective in creating a dark sleep environment. Make sure to install them properly and adjust them to cover the entire window area.
Another useful tip is to layer your window coverings. You can combine curtains with blinds to create an extra layer of darkness. This can further minimize the entrance of light into your bedroom.
While choosing curtains or blinds, it's essential to also pay attention to their color. Dark-colored curtains or blinds are more effective in blocking out light compared to lighter-colored ones. Dark colors absorb light, while light colors reflect it.
In addition to selecting the right curtains or blinds, it's important to ensure they are properly maintained. Regularly clean and dust them to prevent any build-up that could impact their effectiveness in blocking out light.
By using curtains or blinds effectively, you can significantly reduce the amount of external light that enters your bedroom and create a dark sleep environment that promotes better sleep.
Wearing an Eye Mask
Wearing an eye mask is a simple yet effective method to sleep better in the dark. By blocking out external light sources, an eye mask helps create a darker sleep environment, which is essential for quality sleep.
One of the main benefits of wearing an eye mask is that it can help regulate your circadian rhythm. The circadian rhythm is the internal clock that regulates our sleep-wake cycle, and it is heavily influenced by light. By blocking out light, especially blue light from electronic devices, the eye mask promotes the release of melatonin, a hormone that helps us fall asleep and stay asleep.
When choosing an eye mask, it is important to select one that is comfortable and fits securely. A mask that is too tight or too loose can cause discomfort and affect the quality of your sleep. Look for masks made from soft, breathable materials, such as silk or cotton, that won't irritate your skin or trap heat.
Using an eye mask is particularly beneficial for individuals who sleep during the day or in brightly lit environments. It can also be useful for frequent travelers who need to sleep in different time zones or in places with unfamiliar lighting conditions.
To enhance the effectiveness of the eye mask, it is recommended to combine it with other methods to create a dark sleep environment. This can include using blackout curtains or blinds to block out external light, and avoiding the use of electronic devices before bedtime.
Avoiding Electronic Devices Before Bed
Avoiding Electronic Devices Before Bed
Electronic devices, such as smartphones, tablets, laptops, and televisions, have become an integral part of our daily lives. However, the blue light emitted by these devices can have a significant impact on our sleep quality and overall health.
Blue light has a higher frequency and shorter wavelength compared to other colors in the light spectrum. It suppresses the secretion of melatonin, a hormone that regulates the sleep-wake cycle. Exposure to blue light before bed can disrupt this cycle, making it difficult to fall asleep and stay asleep throughout the night.
There are several reasons why avoiding electronic devices before bed can be beneficial for getting a good night's sleep:
- Reduced Exposure to Blue Light: By avoiding electronic devices, especially those with screens, you reduce your exposure to blue light. This allows your body to naturally produce melatonin, promoting better sleep.
- Improved Sleep Quality: The quality of your sleep can greatly improve when you limit your exposure to electronic devices before bed. Blue light not only affects the duration of your sleep but also the depth and quality of your sleep cycles.
- Enhanced Relaxation: Engaging with electronic devices, whether through work-related tasks or social media, can stimulate your brain and make it difficult to relax and unwind. By avoiding these devices before bed, you create a more calming environment conducive to sleep.
If you find it challenging to avoid electronic devices entirely before bed, there are a few strategies you can implement to minimize their impact:
- Establish a Digital Curfew: Set a specific time, ideally one to two hours before bedtime, when you stop using electronic devices. This allows your body to gradually wind down and transition into a more sleep-friendly state.
- Use Night Mode or Blue Light Filters: Many electronic devices have built-in features like night mode or blue light filters that reduce the amount of blue light emitted. Enable these settings to minimize the impact on your sleep.
- Engage in Relaxing Activities: Instead of scrolling through social media or watching TV before bed, engage in activities that promote relaxation, such as reading a book, taking a warm bath, or practicing mindfulness and meditation.
Avoiding electronic devices before bed is a simple yet effective step towards improving your sleep quality and overall well-being. By implementing these strategies, you can create a more conducive sleep environment and enjoy the benefits of a restful night's sleep.





