1. Introduction to Magnesium Allergy
Magnesium allergy is a condition where the body's immune system reacts negatively to the presence of magnesium compounds. Magnesium is a mineral that is essential for various bodily functions, including muscle relaxation, nerve function, and energy production. However, for some individuals, exposure to magnesium can trigger an allergic response.
In this section, we will discuss the causes, prevalence, symptoms, diagnosis, types, and treatment options for magnesium allergy. We will also explore the serious and common side effects of magnesium compounds, as well as the role of magnesium in specific health conditions.
Now, let's delve into the details of magnesium allergy and gain a better understanding of this condition.
Cause of magnesium allergy
Magnesium allergy, also known as magnesium hypersensitivity, occurs when the immune system reacts abnormally to the presence of magnesium in the body. While magnesium is an essential mineral necessary for various bodily functions, some individuals may develop an allergic reaction to it. Understanding the causes of magnesium allergy can help in prevention and management of this condition.
One of the main causes of magnesium allergy is a hypersensitivity reaction triggered by the body's immune system. When exposed to magnesium, the immune system may identify it as a foreign substance and launch an allergic response. The exact reasons why some individuals develop an allergy to magnesium are not fully understood, but certain factors may increase the risk.
Genetics may play a role in the development of magnesium allergy. People with a family history of allergies or allergic conditions are more likely to be prone to magnesium allergies. Additionally, individuals with a history of other allergies, such as pollen or food allergies, may be more susceptible to developing magnesium allergy.
Excessive exposure to magnesium compounds can also increase the risk of developing an allergic reaction. This can occur through various sources, including dietary supplements, medications, and topical applications. Repeated exposure to high levels of magnesium compounds can sensitize the immune system and lead to the development of an allergy.
Furthermore, certain health conditions can contribute to the development of magnesium allergy. Individuals with asthma or other respiratory conditions are more likely to develop an allergic reaction to magnesium. Additionally, individuals with weakened immune systems or underlying autoimmune disorders may have an increased risk of magnesium hypersensitivity.
It is important to note that allergic reactions to magnesium are relatively rare. Most individuals can tolerate normal levels of magnesium intake without any adverse effects. However, for those who do develop an allergy, identifying the specific cause is crucial in managing the condition.
Prevalence of magnesium allergy
Magnesium allergy is a relatively rare condition, but it can occur in certain individuals who are hypersensitive to this mineral. The prevalence of magnesium allergy varies depending on factors such as geographical location, genetics, and exposure to magnesium-containing substances.
Although precise statistics on the prevalence of magnesium allergy are limited, studies suggest that the prevalence is low, with only a small percentage of individuals experiencing allergic reactions to magnesium compounds. Research has shown that the prevalence of magnesium allergy ranges from approximately 1% to 3% of the population.
It is important to note that the prevalence of magnesium allergy may differ based on the specific type of magnesium compound. For example, allergies to magnesium chloride and magnesium stearate are relatively rare, whereas magnesium in skin allergy may be more common.
The prevalence of magnesium allergy can also vary among different patient populations. For instance, individuals with pre-existing allergies or sensitivities to other substances may be more susceptible to developing an allergic reaction to magnesium. Additionally, individuals with certain underlying medical conditions, such as asthma or eczema, may have a higher risk of magnesium allergy.
Furthermore, exposure to certain occupational settings or environments can increase the likelihood of developing magnesium allergy. For instance, workers in industries that involve regular contact with magnesium compounds, such as manufacturing or construction, may be at a higher risk.
It is worth mentioning that the prevalence of magnesium allergy should not be confused with magnesium deficiency, which is a separate condition that occurs when the body does not have enough magnesium. While magnesium deficiency is relatively common, allergic reactions to magnesium are rare.
Overall, although magnesium allergy is not as prevalent as some other types of allergies, it is essential to be aware of its existence and potential risks. If you suspect you may have a magnesium allergy, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for appropriate diagnosis and guidance.
Symptoms of magnesium allergy
Magnesium allergy can manifest in various symptoms that can affect different parts of the body. If you suspect that you may have a magnesium allergy, it's important to be aware of the potential symptoms. Here are some common symptoms associated with magnesium allergy:
- Skin reactions: Skin reactions are a common symptom of magnesium allergy. These reactions can vary from mild itching and redness to more severe rashes and hives. In some cases, skin reactions may also lead to swelling and blistering.
- Respiratory issues: Allergies to magnesium can also affect the respiratory system, causing symptoms such as coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath, and chest tightness. These symptoms can range from mild to severe and may be triggered by inhalation or exposure to magnesium compounds.
- Gastrointestinal problems: Some individuals with magnesium allergy may also experience gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. These symptoms can occur after ingesting foods or medications containing magnesium.
- Cardiovascular symptoms: In rare cases, magnesium allergy can lead to cardiovascular symptoms such as irregular heartbeats, palpitations, and low blood pressure. If you experience any of these symptoms after magnesium exposure, seek immediate medical attention.
- Muscle and joint pain: Magnesium allergy can cause muscle and joint pain, which may be accompanied by stiffness and swelling. These symptoms can significantly affect mobility and daily activities.
If you experience any of these symptoms after being exposed to magnesium, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment. Keep in mind that these symptoms may also be caused by other factors, so a thorough evaluation is necessary to confirm magnesium allergy.
Diagnosis of magnesium allergy
Diagnosing a magnesium allergy can be challenging, as it requires a thorough evaluation of symptoms and medical history. If you suspect a magnesium allergy, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis.
The diagnostic process for magnesium allergy typically involves the following:
- Medical History: Your healthcare provider will start by asking about your symptoms and any possible triggers that may be causing your allergic reactions. They will also inquire about your medical history and any known allergies.
- Physical Examination: A physical examination may be conducted to check for any visible signs of an allergic reaction, such as skin rashes or hives. Your healthcare provider may also examine your respiratory system if you have reported respiratory symptoms.
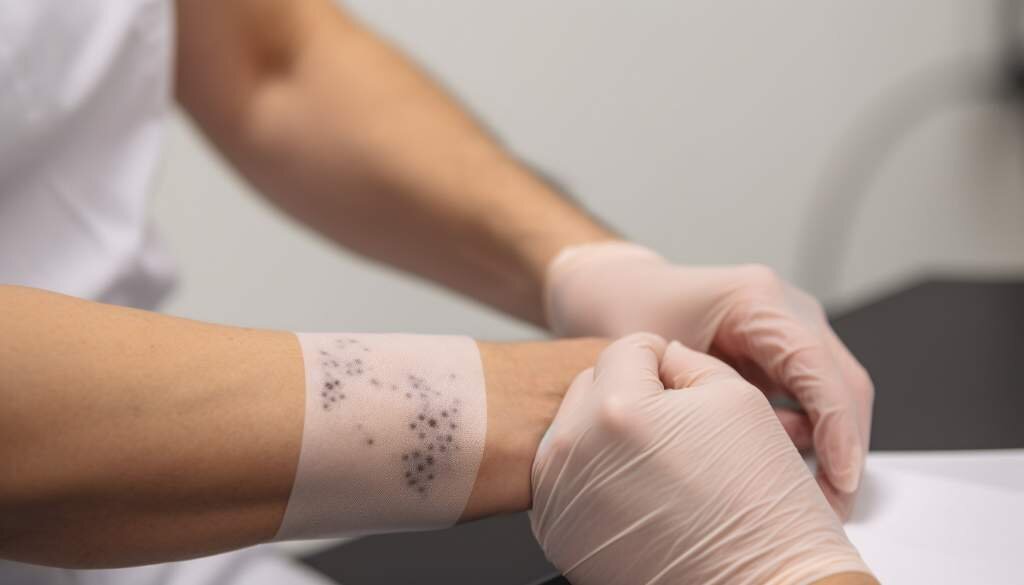
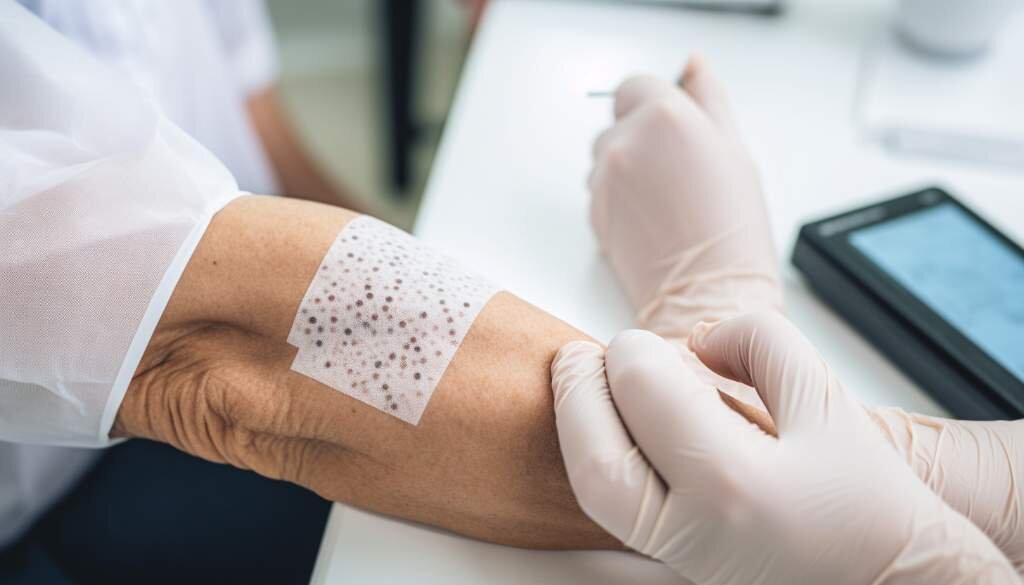
- Allergy Testing: Allergy testing can help determine if you have a magnesium allergy. Two common types of allergy tests are:
- Skin Prick Test: In this test, small amounts of magnesium are pricked onto your skin, usually on your forearm or back. If you are allergic to magnesium, you will experience an allergic reaction at the site of the prick, such as redness, swelling, or itching.
- Blood Test: A blood test, known as a specific IgE test, can measure the levels of magnesium-specific antibodies in your blood. High levels of these antibodies indicate an allergic response to magnesium.
Based on the results of these tests, your healthcare provider can confirm whether you have a magnesium allergy. It is important to note that these tests should be conducted under the guidance of a healthcare professional, as they can best interpret the results and provide a proper diagnosis.

2. Types of Magnesium Allergies
When it comes to magnesium allergies, there are different types that can occur. These allergies are characterized by the body's adverse reaction to various forms of magnesium compounds. Understanding the different types of magnesium allergies is essential for proper diagnosis and management.
In this section, we will explore the different types of magnesium allergies without going into specific details. Subsequent subsections will delve deeper into each type to provide a comprehensive understanding. Here are the types of magnesium allergies that we will cover:
- Magnesium in skin allergy
- Magnesium chloride allergy
- Magnesium stearate allergy
By exploring these different types of magnesium allergies, you will gain a better understanding of the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options available. Let's now dive into each type and gain a deeper insight.
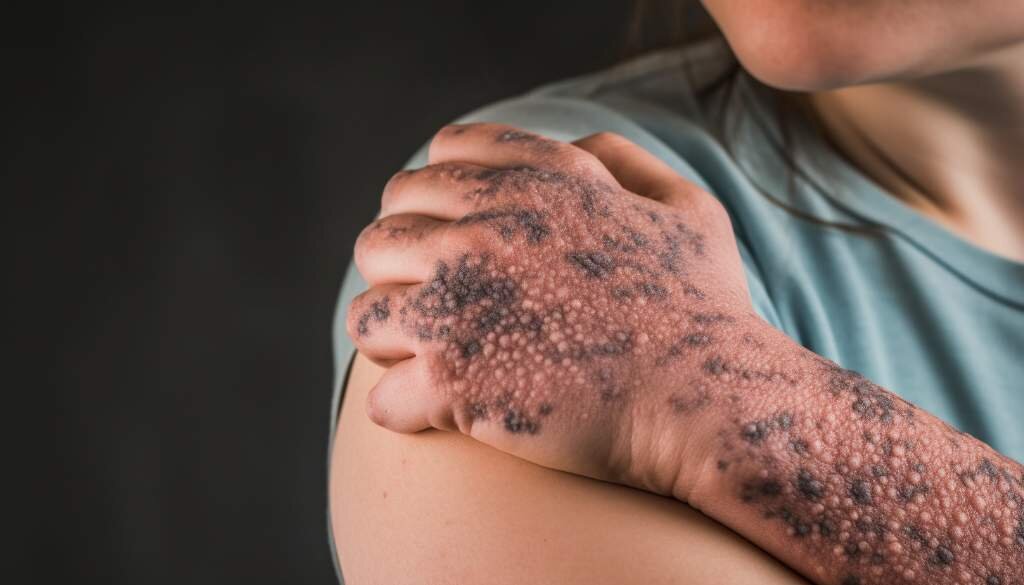
Magnesium in skin allergy
Magnesium in skin allergy is a specific type of magnesium allergy that affects the skin. It is characterized by an allergic reaction to the application or exposure of magnesium-based products on the skin.
One common cause of magnesium in skin allergy is the use of topical creams or lotions that contain magnesium compounds. These products can trigger an allergic response in individuals who are sensitive to magnesium. The allergic reaction may present as redness, itching, swelling, or even a rash on the skin.
Another cause of magnesium in skin allergy is exposure to magnesium-based substances in the environment. This can occur through contact with certain objects or materials that contain magnesium, such as metal alloys or magnesium-rich soil.
Individuals with magnesium in skin allergy may experience a range of symptoms. These can include irritation, itching, redness, and swelling of the skin. In some cases, the allergic reaction can be severe and lead to blistering or the formation of hives.
Diagnosing magnesium in skin allergy involves a comprehensive evaluation of the individual's medical history and symptoms. A dermatologist may conduct a thorough physical examination and may also perform allergy testing, such as patch testing or skin prick testing, to identify the specific allergen causing the reaction.
Treatment options for magnesium in skin allergy primarily focus on avoiding exposure to magnesium-based products or substances that trigger the allergic reaction. This may involve carefully reading product labels and avoiding skincare or cosmetic products that contain magnesium compounds.
If an allergic reaction occurs, it is recommended to wash the affected area with mild soap and water to remove any residual magnesium. Applying oatmeal baths, cold compresses, or over-the-counter hydrocortisone creams may help alleviate symptoms such as itching and inflammation.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional or dermatologist for proper diagnosis and guidance on managing magnesium in skin allergy. They can provide personalized recommendations based on the individual's specific symptoms and medical history.
Magnesium chloride allergy
Magnesium chloride allergy is a specific type of magnesium allergy that some individuals may experience. Magnesium chloride is a compound commonly used in various medications, supplements, and topical products. It is known for its therapeutic properties, but for some individuals, it can cause allergic reactions.
When a person is allergic to magnesium chloride, their immune system reacts negatively to the compound. This allergic reaction triggers the release of histamines, resulting in various symptoms. It's important to note that an allergy to magnesium chloride is different from a sensitivity or intolerance.
Symptoms of magnesium chloride allergy can vary from mild to severe and may include:
- Skin reactions: Individuals with a magnesium chloride allergy may experience skin reactions such as redness, itching, rashes, or hives when they come into contact with products that contain this compound.
- Respiratory issues: Some individuals may experience respiratory symptoms such as coughing, wheezing, or shortness of breath when exposed to magnesium chloride.
- Digestive problems: Digestive symptoms like nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea may occur in individuals who are allergic to magnesium chloride.
If you suspect that you have an allergy to magnesium chloride, it is crucial to seek a proper diagnosis from a healthcare professional. Diagnosis is typically done through a combination of a physical examination, medical history review, and allergy testing.
To manage a magnesium chloride allergy, the primary step is to avoid exposure to products that contain this compound. This may involve carefully reading labels on medications, supplements, and skincare products. If you are unsure about the presence of magnesium chloride in a product, it is recommended to consult with a pharmacist or contact the manufacturer directly.
If you accidentally come into contact with magnesium chloride and experience an allergic reaction, prompt treatment is necessary. Over-the-counter antihistamines can help alleviate mild symptoms. In severe cases, a healthcare professional may prescribe epinephrine or corticosteroids to manage the allergic reaction.
It is worth noting that magnesium chloride allergy is relatively rare, and most people can safely use products containing this compound without any issues. However, if you have a known allergy or have experienced an allergic reaction in the past, it's essential to exercise caution and discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider before using products that contain magnesium chloride.
Magnesium stearate allergy
Magnesium stearate is a commonly used additive in medications, supplements, and various other products. While it is generally regarded as safe, there have been cases of individuals experiencing allergic reactions to magnesium stearate.
A magnesium stearate allergy occurs when the immune system overreacts to the presence of magnesium stearate in the body. This can lead to a range of symptoms and discomfort for those affected.
It is important to note that magnesium stearate allergy is relatively rare compared to other types of magnesium allergies. However, it is still crucial for individuals with known allergies or sensitivities to be cautious when consuming products containing magnesium stearate.
Symptoms of Magnesium Stearate Allergy
When someone is allergic to magnesium stearate, they may experience various symptoms, including:
- Skin rashes or hives
- Itching or irritation
- Swelling, particularly in the face, throat, or tongue
- Shortness of breath
- Chest tightness
- Wheezing or difficulty breathing
- Digestive issues like nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea
It is essential to note that these symptoms can vary in severity and may be different for each individual.
Diagnosing Magnesium Stearate Allergy
Accurately diagnosing a magnesium stearate allergy can be challenging, as the symptoms may overlap with other allergies or intolerances. A healthcare professional, such as an allergist or dermatologist, can help determine if magnesium stearate is the cause of an individual's allergic reactions.
A doctor may conduct a physical examination, review the patient's medical history, and perform or recommend tests such as skin patch testing or blood tests to identify the specific allergen.
Managing Magnesium Stearate Allergy
If someone has confirmed a magnesium stearate allergy, the most effective way to manage it is to avoid products that contain magnesium stearate. This can involve carefully reading labels and selecting alternative products that do not contain this additive.
In cases where magnesium stearate is present in medications prescribed by a doctor, it is crucial to inform the healthcare provider about the allergy. They can then suggest alternative medications or work with a compounding pharmacy to create a customized formulation without magnesium stearate.
If an individual accidentally consumes a product containing magnesium stearate and experiences a severe allergic reaction, they should seek emergency medical attention immediately.
Overall, while magnesium stearate allergy is not very common, it is still vital for individuals with known allergies or sensitivities to be aware of its presence in various products and take appropriate precautions.

3. Serious Side Effects of Magnesium Compounds
Serious side effects of magnesium compounds can occur in some individuals, highlighting the importance of understanding the potential risks associated with these substances. Magnesium compounds, such as magnesium chloride and magnesium oxide, are commonly used for various health purposes, including improving magnesium levels in the body. However, it is crucial to be aware of the serious side effects that can occur from the use of these compounds.
In this section, we will explore the serious side effects of magnesium compounds in more detail. We will discuss the potential risks and hazards associated with magnesium chloride and magnesium oxide. It's essential to have a comprehensive understanding of these side effects to make informed decisions regarding the use of magnesium compounds.
Within this section, we will address several subtopics related to the serious side effects of magnesium compounds. These subtopics will cover the specific side effects of magnesium chloride and magnesium oxide, their potential risk factors, and how to manage and prevent severe magnesium allergies. Understanding these aspects will enable individuals to navigate the potential risks associated with magnesium allergies effectively.
Serious side effects of magnesium chloride
Magnesium chloride is a commonly used compound that can have serious side effects in certain individuals. While it is generally well-tolerated, some people may experience adverse reactions when using magnesium chloride. It is important to be aware of these side effects, as they can vary in severity.
1. Gastrointestinal Disturbances: One of the most common side effects of magnesium chloride is gastrointestinal disturbances. This can include symptoms such as diarrhea, nausea, and stomach cramps. These side effects occur because magnesium chloride can stimulate the muscles of the gastrointestinal tract, leading to increased motility and bowel movements.
2. Electrolyte Imbalances: Magnesium chloride can disrupt the balance of electrolytes in the body. This can lead to low levels of other essential minerals, such as calcium and potassium. Electrolyte imbalances can cause symptoms like muscle weakness, fatigue, irregular heartbeat, and even seizures in severe cases.
3. Allergic Reactions: Although rare, some individuals may develop an allergic reaction to magnesium chloride. Allergic reactions can range from mild skin rashes to more severe symptoms like difficulty breathing and swelling of the face, lips, or tongue. If you experience any signs of an allergic reaction, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention.
4. Kidney Problems: Prolonged use of magnesium chloride or high doses of the compound can potentially lead to kidney problems. This is especially true for individuals with pre-existing kidney conditions. Symptoms of kidney problems may include changes in urine output, swelling in the legs or ankles, and fatigue. It is important to consult a healthcare professional if you experience any kidney-related symptoms.
5. Cardiovascular Effects: In some cases, magnesium chloride can affect the cardiovascular system. It can cause vasodilation, which is the widening of blood vessels. This can lead to a drop in blood pressure. Individuals with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions should use magnesium chloride with caution and under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
It is important to note that while these side effects can occur, they are not common for most individuals using magnesium chloride. If you are concerned about potential side effects, it is advisable to consult with your healthcare provider before starting any magnesium chloride supplement.
Serious side effects of magnesium oxide
Magnesium oxide is a commonly used magnesium compound that is known to have some serious side effects. While it is primarily used as a dietary supplement to provide adequate levels of magnesium in the body, it is essential to be aware of its potential adverse effects.
One of the serious side effects of magnesium oxide is gastrointestinal distress. In some individuals, taking magnesium oxide orally can cause diarrhea, abdominal cramps, and bloating. These symptoms are more likely to occur when magnesium oxide is taken in high doses or when an individual has a sensitive digestive system.
In rare cases, magnesium oxide can also lead to an allergic reaction. Although allergies to magnesium oxide are not very common, they can manifest as skin rashes, itching, swelling, or difficulty breathing. If you experience any of these symptoms after taking magnesium oxide, it is crucial to seek medical attention immediately.
Another potential serious side effect of magnesium oxide is its impact on certain medications. Magnesium oxide can interfere with the absorption of some medications, such as antibiotics, thyroid medications, and certain heart medications. Therefore, it is important to inform your healthcare provider about any magnesium oxide supplementation to ensure the efficacy of other medications.
Additionally, long-term use of high doses of magnesium oxide can lead to magnesium toxicity. This condition, known as hypermagnesemia, can cause symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, muscle weakness, confusion, low blood pressure, and irregular heartbeat. It is important to follow the recommended dosage guidelines and consult with a healthcare professional before taking high doses of magnesium oxide.
It is worth mentioning that most individuals can tolerate magnesium oxide without experiencing any serious side effects. However, it is essential to be aware of the potential risks and consult with a healthcare professional if you have any concerns or underlying health conditions.
Risk factors for severe magnesium allergies
Severe magnesium allergies can have serious consequences and it is important to be aware of the risk factors associated with them. While anyone can develop an allergic reaction to magnesium compounds, certain factors increase the likelihood of experiencing a severe allergic response.
One major risk factor is having a known history of allergies. People who have a history of allergies to other substances, such as pollen, pet dander, or certain medications, may be more prone to developing severe magnesium allergies. This is because their immune system is already sensitized and more likely to overreact when exposed to potential allergens.
Another risk factor is previous exposure to magnesium compounds. If someone has previously had an allergic reaction to magnesium or products containing magnesium, the likelihood of experiencing a severe allergic response in the future is higher. It is important to note that even if the previous reaction was mild, it can escalate to a more severe response upon subsequent exposure.
Additionally, individuals with existing respiratory conditions, such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), are at an increased risk of developing severe magnesium allergies. The respiratory system is particularly vulnerable to allergic reactions, and exposure to magnesium compounds can trigger respiratory symptoms, including difficulty breathing, wheezing, and coughing.
A compromised immune system is also a risk factor for severe allergic reactions. People with weakened immune systems, whether due to certain medical conditions or medications that suppress the immune system, may be more susceptible to developing severe allergies to magnesium compounds.
Lastly, it is important to consider individual susceptibility to allergies. Some people simply have a genetic predisposition to developing severe allergic reactions. This means they have a heightened immune response to potential allergens, including magnesium compounds.

4. Other Side Effects of Magnesium Compounds
When taking magnesium compounds, it is important to be aware of the potential side effects they can cause. These side effects, referred to as Other Side Effects of Magnesium Compounds, can vary in severity and impact different individuals in different ways.
In this section, we will explore the various side effects that can arise from using magnesium compounds. From common side effects to managing mild allergies, we will provide you with the necessary information to make informed decisions about your magnesium intake.
Let's delve into the different sub-sections that will be covered:
- Common side effects of magnesium chloride
- Common side effects of magnesium oxide
- Managing mild magnesium allergies
Common side effects of magnesium chloride
Magnesium chloride is a commonly used magnesium compound that can cause certain side effects in some individuals. While magnesium chloride is generally safe for most people, it can have mild to moderate side effects in certain cases.
Common side effects of magnesium chloride may include:
- Diarrhea: Magnesium chloride can have a mild laxative effect, leading to loose stools and diarrhea. This is more likely to occur when taking higher doses of magnesium chloride.
- Upset Stomach: Some individuals may experience stomach discomfort, including nausea, vomiting, and abdominal cramps after taking magnesium chloride.
- Flushing: In some cases, magnesium chloride can cause flushing or a feeling of warmth in the face and skin.
- Low Blood Pressure: Taking high doses of magnesium chloride can potentially lower blood pressure, leading to symptoms such as dizziness, lightheadedness, and fainting.
- Allergic Reactions: While rare, some individuals may have an allergic reaction to magnesium chloride. Symptoms of an allergic reaction may include rash, itching, swelling, dizziness, and difficulty breathing. In severe cases, an allergic reaction to magnesium chloride can lead to anaphylaxis, a life-threatening allergic reaction.
If you experience any of these side effects after taking magnesium chloride, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional. They can provide guidance on whether to continue or adjust the dosage of magnesium chloride and recommend alternative treatment options if needed.
Common side effects of magnesium oxide
Magnesium oxide is commonly used as a supplement to increase magnesium levels in the body. While it can be beneficial for many individuals, there are also some common side effects associated with its use.
One of the most common side effects of magnesium oxide is gastrointestinal discomfort. This can manifest as symptoms such as diarrhea, nausea, and stomach cramps. These symptoms occur because magnesium oxide has a laxative effect, which can lead to an increase in bowel movements.
Another common side effect is a feeling of weakness or fatigue. This may be due to the fact that magnesium oxide can interfere with the body's absorption of other minerals, such as calcium and potassium, which are important for maintaining muscle function and energy levels.
In some cases, individuals may also experience allergic reactions to magnesium oxide. Symptoms of an allergic reaction can include itching, hives, and difficulty breathing. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience any of these symptoms after taking magnesium oxide.
It is worth noting that these side effects are generally mild and transient. They typically resolve on their own once the body adjusts to the supplementation or when the dosage is reduced. However, if you are experiencing severe or persistent side effects, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional.
Managing mild magnesium allergies
Managing mild magnesium allergies involves a combination of lifestyle changes and preventive measures. While mild allergies to magnesium compounds may not be as severe as other allergic reactions, it is still important to take steps to minimize symptoms and avoid any potential complications.
Avoidance of Magnesium:
If you have experienced mild allergic reactions to magnesium compounds, it is essential to avoid products that contain magnesium as much as possible. This includes dietary supplements, medications, and topical products that contain magnesium. Reading product labels carefully and consulting with healthcare professionals can help identify and avoid magnesium-containing products.
Alternative Magnesium Compounds:
If you need magnesium supplementation but have a mild allergy to certain compounds, it is possible to try alternative forms of magnesium. For example, magnesium citrate or magnesium glycinate may be better tolerated by individuals with allergies. However, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before making any changes to your supplement routine.
Identifying Triggers:
Keeping a symptom diary can help identify triggers for your magnesium allergies. By noting down any symptoms experienced after exposure to magnesium-containing products, you can start to recognize patterns and avoid those triggers in the future. This can be especially helpful if you are unsure which specific magnesium compound you are allergic to.
Seeking Medical Advice:
If you are experiencing mild allergic reactions to magnesium or have concerns about managing your allergies, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional. They can provide guidance on how to effectively manage your allergies, recommend alternative medications or treatments if necessary, and ensure that you are taking the appropriate steps to protect your health.
5. Magnesium Allergy Treatment Options
Magnesium Allergy Treatment OptionsMagnesium allergy can cause a range of symptoms and discomfort, but the good news is that there are treatment options available. The treatment options for magnesium allergy aim to alleviate symptoms and manage the allergic reaction to magnesium compounds. This section will explore various treatment options for magnesium allergy.In the following sub-sections, we will discuss the different approaches for managing magnesium allergy. We will take a look at allergy medication specifically designed for magnesium allergies, topical treatments for direct symptom relief, and lifestyle changes that can help prevent future allergic reactions.By examining these treatment options, we can gain a better understanding of how to effectively mitigate the symptoms of magnesium allergy, reduce discomfort, and improve overall quality of life. Let's dive into the sub-sections to learn more about the treatment options available for magnesium allergy.
Allergy medication for magnesium allergies
Allergy medication plays a crucial role in managing magnesium allergies. If you are diagnosed with a magnesium allergy, your doctor may prescribe certain medications to help alleviate symptoms and prevent allergic reactions. Here are some common allergy medications used for treating magnesium allergies:
- Antihistamines: These medications work by blocking the effects of histamine, a substance released by the immune system during an allergic reaction. Antihistamines can help relieve symptoms such as itching, hives, and sneezing caused by magnesium allergies.
- Corticosteroids: Corticosteroids, either in topical or oral form, are prescribed to reduce inflammation caused by magnesium allergies. These medications can help relieve symptoms such as redness, swelling, and itching. Oral corticosteroids may be prescribed for severe allergic reactions.
- Epinephrine: Epinephrine, also known as adrenaline, is a hormone that can be injected to treat severe allergic reactions. It works quickly to relax the airway muscles and improve breathing, while also reducing swelling and hives. Epinephrine is commonly used in cases of anaphylaxis, a severe and potentially life-threatening allergic reaction.
It is important to follow your doctor's instructions and take the prescribed allergy medication as directed. If you experience any side effects or have concerns about the medication, be sure to discuss them with your doctor.
Topical treatments for magnesium allergies
Topical treatments for magnesium allergies involve using products that are applied directly to the skin. These treatments can help alleviate symptoms and provide relief for individuals with magnesium allergies. Here are some commonly used topical treatments for magnesium allergies:
- Corticosteroid Creams: These creams contain corticosteroids, which are anti-inflammatory medications. They can help reduce redness, itching, and swelling caused by magnesium allergies. Applying corticosteroid creams to the affected area can provide immediate relief.
- Calamine Lotion: Calamine lotion is a soothing topical treatment that can help relieve itching and irritation caused by magnesium allergies. It contains ingredients like zinc oxide and ferric oxide, which have anti-itch and anti-inflammatory properties.
- Antihistamine Creams: Antihistamine creams contain antihistamines, which can block the release of histamines and reduce allergic reactions. These creams are effective in alleviating itching and redness caused by magnesium allergies.
When using topical treatments, it's important to follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer. It's also a good idea to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new treatment. They can provide guidance and recommend the most suitable topical treatment for your specific magnesium allergy symptoms.
Lifestyle changes and prevention
To manage and prevent magnesium allergies, making certain lifestyle changes can be beneficial. These changes can help reduce the risk of developing an allergy and minimize the symptoms. Here are some essential lifestyle modifications to consider:
- Dietary adjustments: Modify your diet to minimize your exposure to magnesium compounds. Identify foods rich in magnesium and avoid them or consume them in moderation. Some common foods high in magnesium include nuts and seeds, dark chocolate, leafy greens, whole grains, and legumes.
- Avoidance of magnesium-containing products: Pay close attention to product labels, especially for medications, cosmetics, and skincare products. Look for alternatives that do not contain magnesium compounds if you are prone to magnesium allergies.
- Magnesium-free alternatives: Explore alternative options for supplements and medications that do not contain magnesium. Consult with your healthcare provider to find suitable alternatives that meet your specific needs.
- Avoidance of environmental triggers: Identify and stay away from environmental triggers that may contain high levels of magnesium. This could include avoiding areas with high levels of dust or pollution where magnesium compounds might be present.
- Consultation with a healthcare professional: If you suspect or have been diagnosed with a magnesium allergy, consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and recommendations. They can offer guidance on managing your condition effectively.
- Regular monitoring: Keep a record of your symptoms and any triggering factors that worsen your magnesium allergy. This will help you identify patterns and make necessary adjustments to your lifestyle.
6. Role of Magnesium in Specific Health Conditions
The role of magnesium in specific health conditions is an important area of study that has gained significant attention in recent years. Magnesium, an essential mineral in the human body, plays a crucial role in various physiological processes. It is involved in hundreds of enzymatic reactions and is necessary for the proper functioning of muscles, nerves, and the cardiovascular system.
In this section, we will explore the potential benefits of magnesium in specific health conditions. We will discuss how magnesium supplementation may play a role in managing and improving symptoms associated with these conditions.
Topics to be covered in the following sub-sections include:
- Magnesium for asthma
- Magnesium for depression
- Magnesium for diabetes
- Magnesium for fibromyalgia
- Magnesium for migraine headaches
- Magnesium for osteoporosis
- Magnesium for preeclampsia
By understanding the role of magnesium in these various health conditions, we can gain insights into potential treatment options and the importance of ensuring adequate magnesium intake.
Magnesium for asthma
Magnesium plays a vital role in many bodily functions and is known for its potential therapeutic benefits in managing various health conditions. One such condition where magnesium has shown promise is asthma.
Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways. It leads to symptoms such as wheezing, coughing, shortness of breath, and chest tightness. Research suggests that magnesium may help alleviate these symptoms and improve asthma control.
Several studies have explored the role of magnesium in asthma management. One aspect is its ability to act as a bronchodilator, which means it helps relax and widen the airways, making it easier to breathe.
Intravenous magnesium sulfate has been used in emergency asthma treatment to relieve acute symptoms and improve lung function. It is administered in severe asthma attacks that do not respond well to standard bronchodilator medications.
Besides its emergency use, magnesium can also be used as a long-term treatment option for chronic asthma. Some studies suggest that magnesium supplementation, either through diet or supplements, may help reduce the frequency and severity of asthma exacerbations.
However, it's important to note that the evidence for the effectiveness of magnesium in asthma management is mixed. While some studies have shown positive results, others have not found significant benefits. More research is needed to determine the optimal dosage, duration, and efficacy of magnesium supplementation for asthma.
In addition to its bronchodilator effects, magnesium may also have anti-inflammatory properties. Asthma is characterized by airway inflammation, and magnesium's potential anti-inflammatory effects could help reduce inflammation and improve asthma control.
It's worth mentioning that magnesium should not be used as a replacement for standard asthma medications. It should be viewed as a complementary therapy that can potentially enhance asthma management when used in conjunction with prescribed medications.
Before considering magnesium supplementation for asthma, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional. They can evaluate your specific case and provide personalized recommendations based on your individual needs. They can also guide you on the proper dosage and help monitor for any potential interactions or side effects.
In conclusion, while magnesium has shown promise in asthma management, it should be used as an adjunct therapy alongside standard medications. It may help improve asthma control by acting as a bronchodilator and potentially reducing airway inflammation. However, further research is needed to establish its optimal use and effectiveness in asthma treatment.
Magnesium for depression
Magnesium has been found to play a crucial role in mental health, including the management of depression. Several studies have shown that magnesium deficiency is associated with an increased risk of developing depression and that supplementing with magnesium can help alleviate symptoms. Here are some key points about the role of magnesium in depression:
- Magnesium and neurotransmitters: Magnesium is involved in the regulation of neurotransmitters, which are chemicals responsible for transmitting signals in the brain. Low magnesium levels can disrupt the balance of neurotransmitters, including serotonin, which is often referred to as the ‘feel-good' hormone. By increasing magnesium levels, it is possible to restore the normal functioning of neurotransmitters and improve mood.
- Magnesium and stress: Chronic stress is known to deplete magnesium levels in the body. This depletion can further contribute to the development of depression. Magnesium plays a vital role in regulating the stress response and reducing the production of stress hormones, such as cortisol. By maintaining adequate magnesium levels, individuals may be better equipped to cope with stress and reduce their risk of depression.
- Magnesium and inflammation: Inflammation has been linked to the development of depression. Magnesium possesses anti-inflammatory properties and can help reduce inflammation in the body. By reducing inflammation, magnesium may alleviate symptoms of depression and improve overall mental well-being.
- Research evidence: Multiple studies have investigated the impact of magnesium supplementation on depression. These studies have shown promising results, with some suggesting that magnesium can be as effective as certain antidepressant medications. However, more research is needed to confirm these findings and determine the ideal dosage of magnesium for depression.
- Forms of magnesium: There are various forms of magnesium supplements available, such as magnesium citrate, magnesium glycinate, and magnesium threonate. Each form has different absorption rates and bioavailability. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable form of magnesium for treating depression.
- Considerations: While magnesium supplementation may be beneficial for depression, it is essential to recognize that it is not a standalone treatment. It can be used as part of a holistic approach that includes therapy, lifestyle changes, and other interventions as recommended by a healthcare professional.
Magnesium for diabetes
Magnesium is an essential mineral that plays a crucial role in many bodily functions, including blood sugar regulation. Research suggests that magnesium deficiency may contribute to the development and progression of diabetes. In this section, we will explore the potential benefits of magnesium for diabetes management.
1. Blood Sugar Regulation:
Magnesium is involved in insulin secretion and insulin action, which are essential for maintaining normal blood sugar levels. It helps to transport glucose into cells, where it can be used for energy. Studies have shown that magnesium supplementation can improve insulin sensitivity and help regulate blood glucose levels in individuals with diabetes.
2. Insulin Resistance:
Insulin resistance is a condition in which the body's cells become less responsive to the effects of insulin, leading to high blood sugar levels. Magnesium supplementation may help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce insulin resistance, consequently promoting better blood sugar control in individuals with diabetes.
3. Cardiovascular Health:
Individuals with diabetes are at an increased risk of developing cardiovascular complications. Magnesium has been shown to have cardioprotective effects by reducing inflammation, improving endothelial function, and regulating blood pressure. These benefits contribute to the overall cardiovascular health of individuals with diabetes.
4. Neuropathy Prevention:
Diabetes-related neuropathy is a common complication characterized by damage to the nerves. Research suggests that magnesium supplementation may help prevent or alleviate diabetic neuropathy due to its role in nerve function and protection against oxidative stress.
5. Glycemic Control:
Proper glycemic control is crucial for individuals with diabetes to prevent complications. Studies have shown that magnesium supplementation can significantly improve glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels, a marker of long-term blood sugar control. This indicates that magnesium may play a role in overall glycemic control.
It's important to note that while magnesium supplementation may have potential benefits for individuals with diabetes, it should not be used as a substitute for conventional medical treatments. It is always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplements or making significant changes to your diabetes management plan.
Magnesium for fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia is a chronic disorder characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, and tenderness in specific areas of the body. It is estimated to affect approximately 2-8% of the population worldwide. While the exact cause of fibromyalgia is unknown, researchers have discovered a potential link between magnesium levels and fibromyalgia symptoms.
Studies have shown that individuals with fibromyalgia often have lower levels of magnesium in their bodies compared to those without the condition. Magnesium plays a crucial role in muscle function, nerve transmission, and energy production. Deficiencies in magnesium can lead to muscle pain, cramps, and fatigue, which are common symptoms experienced by fibromyalgia patients.
Supplementing with magnesium has been found to have potential benefits for individuals with fibromyalgia. The use of magnesium as a dietary supplement or through transdermal applications such as magnesium oil or Epsom salt baths has shown promising results in reducing pain, improving sleep quality, and alleviating fatigue associated with fibromyalgia.
One study found that fibromyalgia patients who received magnesium supplementation experienced a significant reduction in pain levels and tender point counts compared to those who received a placebo. Another study reported improvements in muscle strength and a decrease in the number of tender points with magnesium supplementation.
It's important to note that while magnesium supplementation may provide relief for some fibromyalgia symptoms, it may not be a cure-all solution. Fibromyalgia is a complex condition that requires a multidimensional approach to treatment, including lifestyle changes, medication, and therapies tailored to individual needs.
If you're considering using magnesium supplements for fibromyalgia, it's crucial to consult with a healthcare professional or a knowledgeable practitioner. They can guide you on the appropriate dosage, potential interactions with other medications, and any possible side effects.
Magnesium for migraine headaches
Magnesium has been found to be an effective treatment option for migraine headaches. Migraine headaches are a debilitating type of headache characterized by intense pain, throbbing, and sensitivity to light and sound. They can significantly impact an individual's quality of life and productivity.
Several studies have shown that magnesium supplementation can help reduce the frequency and severity of migraine attacks. Magnesium is involved in various biochemical processes in the body, including the regulation of nerve function and neurotransmitter release. A deficiency in magnesium levels has been implicated in the development of migraines.
Research suggests that magnesium may help by stabilizing blood vessels, reducing inflammation, and calming overactive nerve cells that contribute to migraines. It may also have a protective effect on the brain, minimizing oxidative stress and neuronal damage.
When it comes to migraine treatment, magnesium citrate and magnesium oxide are commonly used forms of magnesium supplements. These forms are easily absorbed by the body and have been shown to be effective in reducing the frequency and intensity of migraines.
It's important to note that while magnesium supplementation can be beneficial, it is not a standalone treatment for migraines. It is often used in combination with other therapies, such as lifestyle modifications, stress management techniques, and other medications.
If you suffer from migraines, it is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any magnesium supplementation. They can assess your individual needs and help determine the appropriate dosage and form of magnesium for you. They will also consider any potential interactions with other medications you may be taking.
In conclusion, magnesium supplementation has shown promise in the treatment of migraine headaches. Along with other therapeutic approaches, magnesium can help reduce the frequency and severity of migraines, improving the overall quality of life for those affected.
Magnesium for osteoporosis
Magnesium plays a crucial role in maintaining bone health and preventing osteoporosis. Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by weak and brittle bones, making individuals more susceptible to fractures and injuries. Adequate magnesium intake is essential for the proper development and maintenance of bone tissue.
Magnesium helps in the absorption and metabolism of calcium, which is the primary mineral required for bone strength. It promotes the production of calcitonin, a hormone that helps regulate calcium levels in the body. By supporting calcium absorption, magnesium aids in the formation of new bone cells and assists in maintaining bone density.
Studies have shown that low magnesium levels are associated with a higher risk of osteoporosis. Insufficient magnesium intake can lead to impaired bone growth, increased bone loss, and decreased bone mineral density. Therefore, ensuring an adequate intake of magnesium is crucial for preventing or managing osteoporosis.
In addition to its role in calcium metabolism, magnesium also helps regulate vitamin D levels in the body. Vitamin D is essential for optimal bone health as it enhances calcium absorption. Without sufficient magnesium, the body may struggle to maintain adequate vitamin D levels, which can further impact bone health.
It is important to note that while magnesium plays a vital role in preventing osteoporosis, it should be considered as part of a holistic approach to bone health. A balanced diet, regular exercise, and appropriate levels of other nutrients, such as calcium and vitamin D, are also important for maintaining strong and healthy bones.
Overall, ensuring an adequate intake of magnesium through diet or supplementation can contribute to the prevention and management of osteoporosis. However, it is always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice regarding magnesium supplementation and its potential interaction with other medications or health conditions.
Magnesium for preeclampsia
Preeclampsia is a serious condition that can occur during pregnancy and is characterized by high blood pressure and damage to organs such as the liver and kidneys. Magnesium plays a crucial role in the management and treatment of preeclampsia.
Research has shown that administering magnesium sulfate intravenously can help prevent and treat preeclampsia in pregnant women. Magnesium sulfate works by relaxing blood vessels, improving blood flow to the placenta, and reducing the risk of seizures.
Women who are at high risk of developing preeclampsia, such as those with a history of the condition or chronic hypertension, may be given magnesium sulfate as a preventative measure. This helps to lower the chances of developing severe preeclampsia and its complications.
In addition to its role in preventing preeclampsia, magnesium also plays a part in the management of the condition. Magnesium sulfate is often used to control blood pressure in women with preeclampsia, reducing the risk of complications. It can also help to prevent preterm labor in women with preeclampsia.
It is important to note that the use of magnesium sulfate for preeclampsia should only be done under medical supervision. The dosage and administration method will depend on the individual's condition and medical history.







