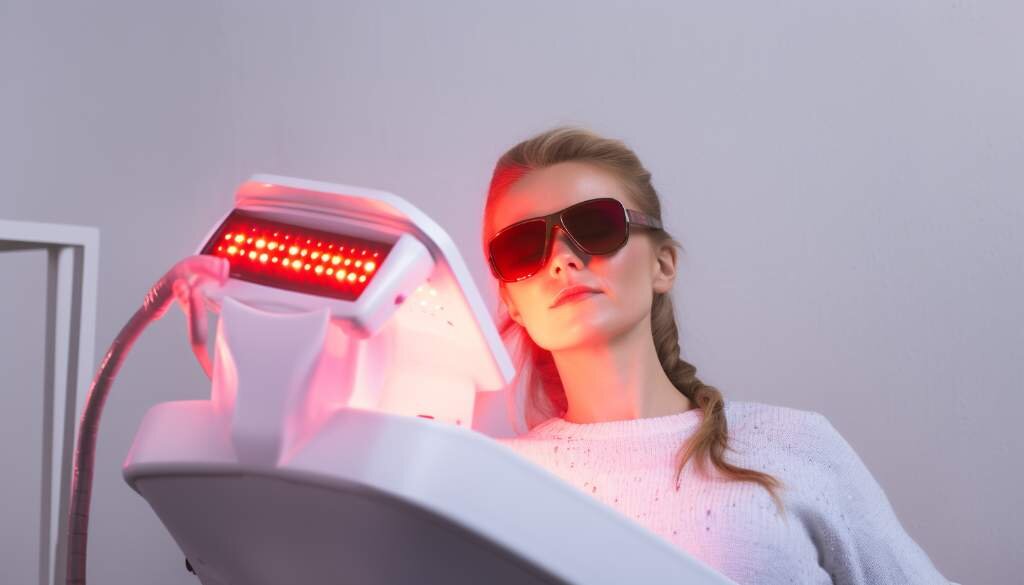

Overview of Light Therapy for Psoriasis
Light therapy, also known as phototherapy, is a common treatment for psoriasis that involves exposing the skin to ultraviolet (UV) light. It is primarily used to alleviate the symptoms of psoriasis, including redness, inflammation, and itching.
Light therapy works by slowing down the growth of skin cells and reducing inflammation. The specific wavelengths of light used in phototherapy have been found to be effective in treating psoriasis and other skin conditions.
This section will provide an overview of light therapy for psoriasis and explore its main types and effectiveness. It will also discuss important considerations and potential risks associated with this treatment option. Additionally, we will cover home light therapy options, including their advantages, disadvantages, and safety precautions.
What is Light Therapy for Psoriasis?
Light therapy, also known as phototherapy, is a treatment option for psoriasis that involves the use of ultraviolet (UV) light to manage the symptoms of the condition. It has been found to be particularly effective for psoriasis because UV light exposure can slow down the growth of skin cells and reduce inflammation.
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by the rapid production of skin cells, leading to the development of thick, red, scaly patches on the skin. Light therapy works by targeting the affected areas with UV rays, which penetrate the skin and slow down the excessive cell growth.
UV light can be divided into different types based on their wavelength: UVA, UVB, and narrowband UVB. Each type corresponds to a specific range of wavelengths, with narrowband UVB being the most commonly used in the treatment of psoriasis due to its efficacy and safety.
During a light therapy session, a patient will be exposed to either natural sunlight or artificial UV light in a controlled environment. The duration and frequency of the treatment will vary depending on the severity of the condition and the individual's response.
How Does Light Therapy Work?
Light therapy, also known as phototherapy, is a treatment option for psoriasis that involves exposing the skin to certain types of light. This therapy can help reduce the symptoms of psoriasis and improve overall skin health. Understanding how light therapy works is essential to determine its effectiveness and whether it is a suitable treatment option for you.
Light therapy works by utilizing different wavelengths of light to target the affected areas of the skin. The specific wavelengths used in light therapy have been found to slow down the growth of skin cells and reduce inflammation, which are key factors in psoriasis.
There are various types of light therapy available, including:
- Narrowband UVB therapy (NB-UVB): This type of phototherapy uses a specific wavelength of ultraviolet B (UVB) light that has been proven effective in treating psoriasis.
- Puva therapy: Puva therapy involves combining psoralen, a medication that increases skin sensitivity to light, with UVA light exposure.
- Excimer laser: This laser emits high-intensity UVB light and is commonly used for targeted treatment of psoriasis plaques.
During a light therapy session, the affected areas of the skin are exposed to the light for a specified amount of time. Treatments are typically performed in a dermatologist's office or specialized light therapy centers.
The exact mechanism behind how light therapy works to improve psoriasis is not fully understood. However, it is believed that the light penetrates the skin and affects the immune system cells, reducing their activity and suppressing the inflammation that causes psoriasis.
Light therapy sessions are usually scheduled 2-3 times per week, with the duration and frequency varying depending on the individual's condition and response to treatment. It may take several weeks or months of consistent light therapy sessions to see significant improvement in psoriasis symptoms.
It is important to note that light therapy should always be performed under the guidance of a healthcare professional. They will determine the ideal type and dosage of light therapy based on your specific condition and medical history.
Overall, light therapy is a proven treatment option for psoriasis that can provide relief from symptoms and improve skin health. However, it is essential to discuss the potential benefits and risks with your healthcare provider to determine if light therapy is the right choice for you.
Main Types of Phototherapy
Phototherapy, also known as light therapy, is a popular treatment option for psoriasis. It involves exposing the skin to ultraviolet (UV) light to help reduce the symptoms associated with the condition. There are several main types of phototherapy that can be used to treat psoriasis:
- Narrowband UVB Therapy (NB-UVB): This type of phototherapy uses a specific wavelength of UVB light, known as narrowband UVB, to treat psoriasis. It is considered one of the most effective forms of phototherapy and is commonly used in clinics and hospitals. NB-UVB therapy involves exposing the affected skin to the UVB light for a few minutes, a few times a week. The treatment helps to slow down the excessive growth of skin cells and reduce inflammation, leading to improvements in the symptoms of psoriasis.
- PUVA Therapy: PUVA stands for Psoralen plus Ultraviolet A. This type of phototherapy combines the use of a medication called psoralen, which makes the skin more sensitive to light, with UVA light exposure. Psoralen can be taken orally or applied topically. After taking the medication, the affected skin is exposed to UVA light. PUVA therapy is often used for severe cases of psoriasis or for patients who have not responded well to other treatments. It works by slowing down the growth of skin cells and reducing inflammation.
- Excimer Laser Therapy: Excimer laser therapy is a targeted form of phototherapy that uses a device called an excimer laser to deliver concentrated beams of UVB light to the affected areas of the skin. The laser allows for precise targeting, which can be beneficial for patients with localized areas of psoriasis. Excimer laser therapy is typically performed in a doctor's office or clinic and can provide rapid relief from psoriasis symptoms.
- Goeckerman Therapy: Goeckerman therapy is a combination treatment that involves the use of coal tar and UVB light. The patient applies a coal tar ointment to the affected areas of skin, which is then exposed to UVB light. The coal tar helps to soften and thin the skin, making it more receptive to the UVB light. Goeckerman therapy is often used for patients with severe psoriasis and can be highly effective.
These are the main types of phototherapy used for the treatment of psoriasis. Each type has its own advantages and considerations, so it's important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best approach for your specific condition.
Effectiveness of Light Therapy
Light therapy, also known as phototherapy, has been proven to be an effective treatment option for psoriasis. It involves exposing the skin to ultraviolet (UV) light, which helps reduce inflammation and slow down the rapid growth of skin cells that contribute to psoriasis lesions.
Several studies have shown that light therapy can significantly improve psoriasis symptoms. In fact, it is considered one of the most effective treatments for mild to moderate psoriasis.
UVA and UVB are the two main types of light used in phototherapy. UVA therapy is often used in combination with a medication called psoralen, which makes the skin more responsive to UVA light. This combination is known as PUVA therapy. UVB therapy, on the other hand, does not require any medications.
UVB therapy is considered the most effective form of light therapy for psoriasis. It works by penetrating the outer layers of the skin and slowing down the growth of skin cells. UVB therapy can be administered in different ways, such as through a lamp in a doctor's office or with a home phototherapy unit.
PUVA therapy is typically reserved for people with more severe psoriasis or those who have not responded well to other treatments. It is usually administered in a doctor's office, where the patient takes psoralen either orally or topically before being exposed to UVA light.
Light therapy is often recommended as a first-line treatment for psoriasis because it is generally safe and well-tolerated. However, like any medical treatment, it may not work for everyone. Some individuals may experience minimal improvement or no improvement at all.
Factors that may affect the effectiveness of light therapy include the type and severity of psoriasis, the area of the body being treated, and the individual's response to treatment. It is important to work closely with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate type and duration of light therapy for each individual.
In conclusion, light therapy is a highly effective treatment option for psoriasis. It can help reduce inflammation, slow down the growth of skin cells, and improve overall symptoms. However, it may not work for everyone, and the effectiveness can vary depending on individual factors. Consulting with a healthcare professional is essential to determine the best treatment approach for each person.

Considerations and Risks of Light Therapy
Considerations and Risks of Light Therapy
When considering light therapy as a treatment option for psoriasis, there are important factors to keep in mind. It is essential to understand the potential risks associated with this form of therapy and to consider if it is the right choice for you.
In this section, we will discuss the considerations you should keep in mind before trying light therapy, common side effects you may experience, and the potential risk of skin cancer. Understanding these factors will help you make an informed decision about whether light therapy is suitable for your specific situation.
Continue reading to learn more about what to consider before trying light therapy, the common side effects you may encounter, and the potential risk of skin cancer associated with this treatment.
What to Consider Before Trying Light Therapy
Before trying light therapy for psoriasis, there are several factors to consider to ensure it is the right treatment option for you. These considerations include:
- Type of Psoriasis: Light therapy is typically used to treat plaque psoriasis, so it may not be as effective for other types of psoriasis such as guttate or pustular psoriasis. Make sure to consult with your dermatologist to determine if light therapy is suitable for your specific type of psoriasis.
- Skin Sensitivity: Light therapy involves exposing the skin to UV radiation, which can cause skin sensitivity. If you have sensitive skin or a history of sunburns, it's important to discuss this with your dermatologist before starting light therapy.
- Medical History: Certain medical conditions may make light therapy unsuitable for you. Conditions such as lupus, skin cancer, or a history of melanoma may increase the risk of adverse effects from light therapy. Your dermatologist will evaluate your medical history to determine if light therapy is safe for you.
- Time Commitment: Light therapy requires regular sessions, typically 2-3 times per week, for several weeks or months. Consider your schedule and ability to commit to this treatment regimen before starting light therapy.
- Financial Considerations: Light therapy may involve additional costs, such as travel to a clinic or purchasing a home light therapy device. Check with your insurance provider to see if light therapy is covered and consider the financial implications before making a decision.
By taking these considerations into account, you can make an informed decision about whether light therapy is the right treatment option for your psoriasis.
Common Side Effects of Light Therapy
Light therapy is a commonly used treatment for psoriasis, but like any medical treatment, it comes with potential side effects. It is important to be aware of these side effects before starting light therapy.
One common side effect of light therapy is skin redness and irritation. During the treatment, the skin is exposed to UV light, which can cause the skin to become red and itchy. This usually subsides within a few hours or days after the treatment.
Another possible side effect is dry skin. The UV light used in light therapy can dry out the skin, leading to dryness and flaking. It is important to keep the skin well moisturized during and after the treatment to prevent excessive dryness.
In some cases, light therapy can cause sunburn-like symptoms. This includes redness, blistering, and peeling of the skin. It is important to follow the recommended treatment guidelines and avoid overexposure to UV light to reduce the risk of sunburn.
Light therapy can also cause changes in pigmentation. This means that the treated areas of the skin may become darker or lighter in color. These changes are usually temporary and resolve on their own over time.
In rare cases, light therapy can increase the risk of skin cancer. However, the risk is very low and is usually outweighed by the potential benefits of the treatment. It is important to discuss the risks and benefits of light therapy with your healthcare provider.
If you experience any severe or persistent side effects from light therapy, it is important to contact your healthcare provider. They can provide guidance on how to manage these side effects and may adjust your treatment plan if necessary.
Potential Risk of Skin Cancer
Light therapy, also known as phototherapy, is a common treatment option for psoriasis. While it can be highly effective in managing the symptoms of psoriasis, there are potential risks associated with this treatment, including the risk of developing skin cancer.
The main concern when it comes to the risk of skin cancer with light therapy is the repeated exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation. UV radiation has been linked to an increased risk of developing skin cancer, including both basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma.
It is important to note that the risk of developing skin cancer from light therapy is generally low, especially when the treatment is under the supervision of a healthcare professional. However, individuals with a history of skin cancer or a family history of skin cancer may have a higher risk.
There are several factors that can contribute to the risk of skin cancer from light therapy, including:
- Type of light therapy: Different types of light therapy use different wavelengths of light and varying levels of UV radiation. Narrowband UVB therapy, for example, is considered to have a lower risk of skin cancer compared to other types of light therapy.
- Total cumulative dose: The amount of UV radiation received over time can increase the risk of skin cancer. Healthcare professionals carefully monitor the dose and treatment duration to minimize this risk.
- Skin type: Individuals with fair skin are generally more susceptible to the harmful effects of UV radiation, including the risk of skin cancer.
To minimize the potential risk of skin cancer, it is crucial to follow the recommendations and guidelines provided by your healthcare professional. They will ensure that the treatment plan is tailored to your specific needs and monitor your progress closely.
If you notice any changes in your skin, such as new growths, changes in the appearance of moles, or unusual spots, it is essential to inform your healthcare professional promptly. Regular skin examinations are important to detect any potential skin cancer at an early stage.
It is worth noting that for many individuals, the benefits of light therapy in managing psoriasis outweigh the potential risks of skin cancer. However, it is essential to weigh the pros and cons and make an informed decision in consultation with your healthcare professional.
Home Light Therapy Options
Home light therapy options are a convenient and cost-effective way for individuals with psoriasis to manage their condition from the comfort of their own homes. This treatment involves the use of specialized light devices to expose the affected areas of the skin to specific wavelengths of light, which have been shown to have beneficial effects on psoriasis symptoms.
In the upcoming sub-sections, we will explore the advantages and disadvantages of home light therapy, as well as the safety precautions that need to be followed. By understanding the different aspects of home light therapy, you can make an informed decision about whether it is the right treatment option for you.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Home Light Therapy
Home light therapy for psoriasis offers several advantages and disadvantages that should be considered before choosing this treatment option. Below are some of the major advantages and disadvantages of home light therapy:
Advantages:
- Convenience: One of the main advantages of home light therapy is the convenience it offers. Patients can undergo light therapy sessions in the comfort of their own homes at a time that is convenient for them. This eliminates the need to travel to a medical facility for treatment, saving time and effort.
- Cost Savings: Home light therapy can also be more cost-effective in the long run compared to regular visits to a dermatologist or phototherapy clinic. While the initial investment in a light therapy device may be higher, the overall cost can be lower since there are no ongoing expenses for clinic visits.
- Privacy: Some individuals may feel more comfortable receiving treatment in the privacy of their own homes. Home light therapy allows patients to undergo treatment without others observing their skin condition.
- Prolonged Exposure: With home light therapy, patients have the flexibility to gradually increase their exposure time to light therapy. This can be beneficial for individuals who have sensitive skin and require a slower treatment approach.
Disadvantages:
- Lack of Medical Guidance: Unlike undergoing light therapy in a medical facility under the supervision of a healthcare professional, home light therapy may lack the guidance and expertise of a dermatologist. This can be a potential drawback, as the treatment may not be tailored to the specific needs of the patient.
- Incorrect Usage: Home light therapy devices need to be used correctly to ensure safety and effectiveness. There is a risk of using the device improperly, such as incorrect distance from the skin or improper timing, which may lead to inadequate treatment or potential side effects.
- Limited Options: Home light therapy devices generally offer a limited range of wavelengths and may not be as versatile as the ones used in medical facilities. This means that some individuals may not experience the same level of effectiveness as they would with a more advanced device.
- High Upfront Cost: While home light therapy may be cost-effective in the long run, the initial cost of purchasing a light therapy device can be expensive. This can be a barrier for individuals who are unable to afford the upfront investment.
Safety Precautions for Home Light Therapy
When considering home light therapy for the treatment of psoriasis, it's important to follow certain safety precautions to ensure the effectiveness and safety of the treatment. Here are some key safety precautions to keep in mind:
- Consult with a Dermatologist: Before starting home light therapy, it is crucial to consult with a dermatologist or healthcare professional who can assess your condition and determine if light therapy is suitable for you. They can provide guidance on the best type of light therapy for your specific needs.
- Use FDA-approved Devices: Ensure that the light therapy device you plan to use at home is FDA-approved. This ensures that the device meets certain safety and efficacy standards. Look for devices with a clear FDA approval label.
- Follow Treatment Guidelines: It is essential to carefully follow the treatment guidelines provided by your dermatologist or healthcare professional. This includes the recommended duration and frequency of treatments. Avoid exceeding the recommended time or frequency, as it can lead to adverse effects.
- Protect Your Eyes: Protecting your eyes is crucial during home light therapy. Wear specialized goggles or eye protection that is designed to block out the specific wavelengths of light being used. This helps to prevent potential damage to your eyes.
- Monitor Your Skin: Regularly monitor your skin for any changes or adverse reactions. If you notice any concerning symptoms such as increased redness, blistering, or pain, stop the treatment immediately and consult with your dermatologist.
- Take Breaks: Avoid continuous and prolonged exposure to light therapy. It is important to take breaks between treatments to allow your skin to recover. This helps to minimize the risk of adverse effects such as burning or skin damage.
- Keep Records: Maintain a record of your treatment sessions, including the duration and frequency. This can help you track your progress and provide valuable information to your dermatologist or healthcare professional during follow-up visits.
- Follow Product Instructions: Read and follow the instructions provided with your light therapy device carefully. This includes any safety precautions or warnings mentioned by the manufacturer.
- Be Aware of Potential Risks: Light therapy, even when done at home, can carry certain risks. Be aware of potential side effects and risks associated with light therapy, such as skin irritation, burns, or increased risk of skin cancer. If you have any concerns or questions, consult with your healthcare professional.








